To understand what blockchain is, one needs to imagine a virtual ledger capable of registering and verifying a huge number of electronic transactions quickly and safely. Today, this shared ledger technology has greatly expanded the area of application.
The first blockchain use cases originate from financial institutions and cryptocurrencies called Bitcoin, Litecoin, Ethereum – just to name a few. The annual global market for blockchain development has increased almost trice since 2017 and is going to reach approximately US$16B in the next three years. Industries from healthcare to food to notary are beginning to adopt blockchain. To dive deeper, let’s go back to the basics of the technology.
A blockchain is a file that stores some data. From a technical point of view, it’s a decentralized database, where all data is replicated and shared through multiple computers. No single entity can gain control over the blockchain, be it a federal or a private organization. This unique feature makes the DLT (distributed ledger technology) a revolutionary shift from using centralized and fully administered databases.
Blockchain works this way: the file comprises a series of interconnected pieces of data that create a chain. The great thing about shared ledger tech is that each section of the chain (so-called block) registers any modification of its content, allowing it to create a full history trail that cannot be faked, mislaid, or damaged. This is called an immutable record as a whole.
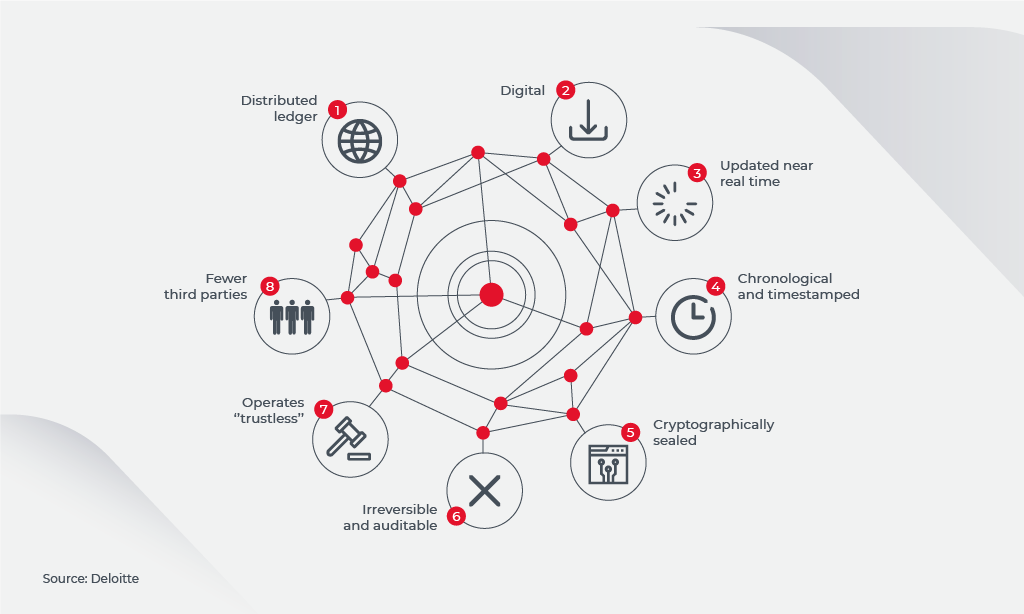
Since the blockchain is replicated across many computers, there can be many users who access the entire chain of data. It’s not a central manager who runs and controls all the transactions or records, but a network of users who collaborate to check the data and reach an agreement. As we mentioned, the first real-world example of applying blockchain is bitcoin, a type of cryptocurrency that works the same way.
Today blockchain has dramatically extended its horizons and went far beyond the cryptocurrencies. It can be applied almost in every aspect of our life. All its advantages stem from the distributed nature and allow for:
1. Registering secure transactions. Record-keeping of payments processing between multiple allies isn’t easy as one two three. Blockchain can reduce obstacles and make relationships smoother. For instance, the result of the collaboration between shipping corporation Maersk and IBM is TradeLens. It’s a blockchain-based shipping platform created to operate global trade more efficiently and securely.
Blockchain-driven shipping platform TradeLens enabled Maersk to consolidate multiple partners, get more transparency over the shared data, and drive market-wide innovation.
2. Managing and securing digital relationships. DLT empowers adopters to benefit from smart contracts, as a perfect solution to monitor and keep visible various business assets such as critical documents of ownership. In essence, these contracts simplify digital interactions while ultimately controlling transactions at the same time. Also, they allow for using automated payments when participants have achieved an agreement on the conditions.
3. Eliminating intermediaries due to the high cost. Real estate providers have to cooperate with clients via a centrally administered platform, like Booking or Airbnb. Blockchain could change all that. For example, an industry-leading travel corporation TUI has started adopting blockchain. It hosts all of its hoteliers on a private blockchain.
TUI executives believe their blockchain platform could eliminate barriers between customers and hotels so that they can directly book suitable accommodation.
4. Keeping track of previous actions. Storing data on the blockchain provides excellent traceability of every alteration made to the datum. This way, the users get the latest updates and manage the entire history of changes, hence the data can’t be changed by an unauthorized person, faked, or unintentionally erased. Users get benefit from tracking history and know about all alterations.
The financial sector was a pioneer in employing blockchain, revealing it’s limitless opportunities for the advancement of global business. Since the mentioned technology has already attracted thousands of organizations to start their transformation, we want to explore the most popular blockchain use cases by industry.
Payments Across Borders
Blockchain offers a reliable and efficient way to create a trail of activities that require enhanced security measures. This tech is the perfect way to process payments internationally and transfer money without worrying about its safety.
Multinational banks UBS and British Barclays are taking blockchain for a spin to streamline back-office operations and settlement, which could potentially decrease US$20B expenses for third-parties involvement.
For example, last year, Barclays invested US$5.5 million in startup Crowdz that helps businesses to promote B2B cash turnover offering alternative ways of payment collection and automation of e-invoices.
On a global scale, blockchain-driven solutions have the purpose of reducing the international transactions’ value, worth 27% of the worldwide transaction market in 2017.
For instance, another renowned Spanish bank has cooperated with the DLT-based company to add visibility to their international payments and dramatically accelerate them.
Insurance
Blockchain delivers outstanding insurance services and value, thanks to smart contracts. These DLT-based contracts enable both clients and insurers to maintain all requests transparently and securely. Since all agreements and clients’ claims are stored on the distributed ledger, the network verifies and approves them getting rid of inaccurate cases.
In 2018, IBM launched a top-notch insurance solution called openIDL with the participation of AAIS, a national insurance advisory company. It’s an open Hyperledger blockchain network that aims to reshape how the data is collected by optimizing insurance regulatory reporting and compliance requirements.
Global Trade
The current global trade’s financial gap has reached almost US$1.5T and can grow up to US$2.4T by 2025. Blockchain can eliminate boundaries and streamline the international business. Thus, distributed ledger technology can potentially facilitate up to US$1.1T of new trade volume, approximately a 30% improvement, thereby dramatically filling the gap.
Blockchain enables stakeholders from different geographic locations to interact more comfortably with each other. International organizations have already started to rewire their legacy systems with the help of DLT. They see the immense impact of this technology in managing global supply chains, running trade finance, and inventing new business models.
Accounting and Auditing
In essence, blockchain-based solutions are very secure, which additionally empowers users to minimize human failures when dealing with accounting or auditing.
Banks continue to adopt cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, and accountants have begun to embrace these technologies, also. They process a significant volume of various papers, from invoices to endless financial spreadsheets, which contain hypersensitive data. Blockchain can help easily handle this critical information.
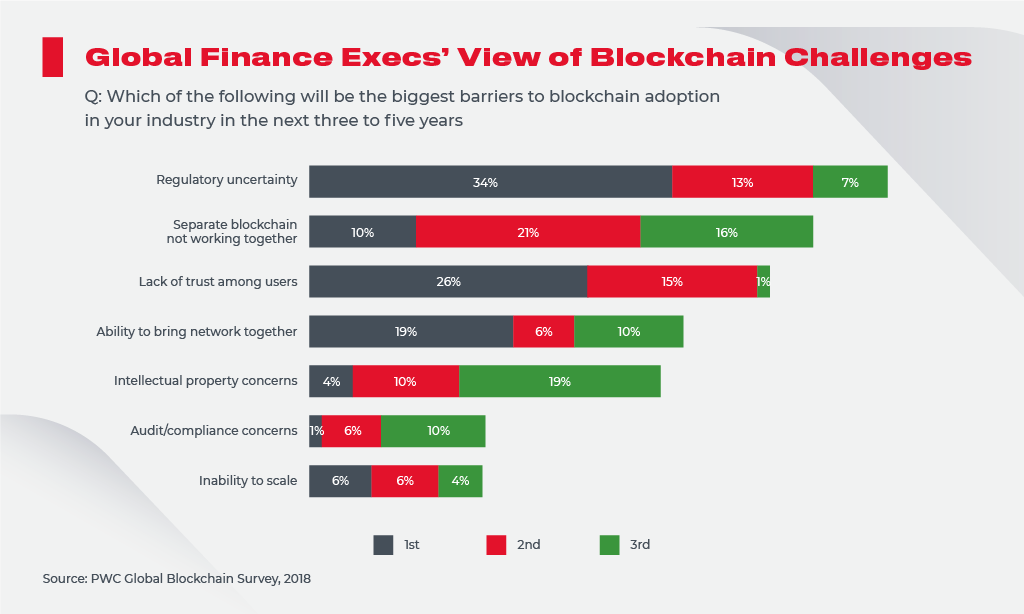
Tracking data powered by DLT may contribute to the automation of some accounting operations using AI, which, in turn, could eliminate employees’ failures and insider fraud.
Giant accounting companies have started leveraging blockchain. For example, PwC launched a new solution supporting audits of cryptocurrency activities. At the same time, the US Patent and Trademark Office awarded KPMG for using the distributed ledger to get secure and error-free data management.
Thanks to the secure digital connection provided by DLT, the popularity of blockchain-driven solutions increasingly grows. Progressive organizations see the numerous benefits in improving their business processes.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain allows for secure, real-time tracking of transactions. Supply chains are mostly a set of transactions that connect to transfer goods from the first destination to the last.
As the goods exchange hands multiple times throughout the supply chain from production to retailer, the blockchain is helpful to document each transaction in an immutable ledger. This way, supply chain executives ensure the security of all payments, minimize delays, cut extra expenses, and reduce employees’ failures.
Healthcare
Healthcare is one of the most vulnerable sectors for cyber attackers. Medical institutions appeared to be unable to share data between providers as well as internally safely.
Secure data distribution between clinics and hospitals can increase the accuracy of diagnoses, the effectiveness of treatments, and overall affordability of care to patients.
The use of blockchain in healthcare enables clinics, patients, and other participants in the collaboration process to give access to their networks without putting critical data at risk.
One AI-based startup in association with IBM created the mobile application to manage personal patients’ data better. The app doesn’t store the health data but allows users to control the access and commercial use of their health records.
Another example of applying DLT is connecting wearables with clinics. The market for these linked to human body devices is supposed to be worth US$14.41 billion by the year 2022.
Healthcare providers are testing wearables to track patients’ health state. These individual devices collect various data such as blood pressure, heartbeat, the quantity of consumed water or food per day, and many more data points. Blockchain can help safely transmit those records to medical representatives by decentralizing stored data and ensuring protected information sharing.
Media
The forecast for worldwide investing in blockchain solutions for the media sector is US$1.54B in the next four years, with an annual 32% increase during 2018-2024.
The growth of the blockchain market in media is caused by further transforming content into the mass-market commodity and growing piracy activities, compromising content security. Plus, there are issues related to third parties that enable the sharing of content between publishers and end-users, leading to costly and unprotected transactions.
Blockchain helps content producers combat these problems and increase their revenues by delivering real-time monetization models. This solution has the potential to cut expenses for payments by 40-80%.
Therefore, without appealing to different vendors, media companies reduce associated costs and save time for all counterparts of the process. The only hurdle on the way of blockchain transformation in the media sector is the lack of standardization and costly implementation efforts.
Real Estate
Throughout life, people are likely to sell their accommodations every five to seven years, while others have a tendency to move nearly twelve times. With such frequent movement, blockchain could be of number one assistant in the real estate deals.
Using customized software solutions based on blockchain for the real estate sector can speed up selling, purchasing, or renting property by ensuring a superfast and protected movement of transactions between stakeholders. Additionally, the blockchain-driven system keeps an eye on the valuable documents.
Elections
To run voting properly, accountable people need to ensure there are the following components: accurate identity authentication, secure votes monitoring, and trustworthy counterparts for votes estimation.
Blockchain devices and platforms can serve during elections as an underlying infrastructure for tracking and tallying votes. This way, the countries’ governments could remove the need for rechecking and prevent electoral fraud, such as fictitious voters and falsifying votes.
By recording votes on the blockchain, governments and electorate would have verified record storage, avoiding human errors and votes compromised by fraudulent social activities.
The real-life examples of blockchain-based organizations include Voatz, a platform that delivers services for government elections, custom events, and convention voting. Votem is another voting platform provider serving private customers and clients from government, public and military sectors.
These companies’ experience shows that blockchain is successfully used to hold secure, electronic elections for government and private purposes.
Non-Business Entities
Many charitable and other non-profit organizations face issues related to insufficient transparency. Blockchain can ensure funding institutions, be it an individual or government sponsorship, that the raised money is safely transferred to the right place.
Federal Taxes and Mail
DLT can facilitate the tedious process of filing taxes. People tend to make many errors during filing, which may result in delays and refiling procedures or even unwanted fines.
The USPS states that they deliver 509 million parcels each day. The OIG report suggests that blockchain can help USPS streamline many processes. For example, the technology can verify each package and mail and recognize the receivers, furthermore approve deliveries to the right people.

For example, each package has a small sensor. Then the blockchain is applied to improve interactions between different USPS partners. Besides, recording packages on a blockchain could promote customs approvals and combine payments, logistics, and transportation into one integrated system. Currently, the United States Postal Service in the investigation stage of leveraging blockchain technology.
Notary Services
Blockchain can improve digital notarization. One of the applications of DLT is that it can prove the existence of the document. The document is stored on the blockchain and is verified by hashing, meaning that any alterations made to it will be instantly recorded and easily tracked by the owner through the timestamps located on this paper.
Besides, employing blockchain smart contracts technology allows document owners to make agreements between participants and track the latest updates to the signed document.
Simply put, a smart contract is used to sign papers, keep track of all modifications, record all signers, and other associated data. It can also store the details about pending, cancellation, approving, and early versions of contracts.
Public Transportation
Modern public transportation systems have become complicated and costly to maintain in cities due to population growth, traffic jams, and inefficient routes.
Utilizing blockchain technology could aid the local city government in optimizing public transportation options. For example, a blockchain-powered company DOVU created the global rewards platform for smart city travelers, underpinned by cryptocurrency. The application allows customers to get rewarded with DOV tokens for sharing and facilitating the commuting. Also, it enables mobility providers to interact with the users closely and know their demand better. This way, the cities get their transportation issues resolved.
Blockchain can also help track the transport’s effectiveness in real time, adapt the schedules if needed, and streamline routes.
Additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing or 3D printing uses CAD (computer-aided design) model or 3D object to create an object layer upon layer with a particular geometric form. The term ‘’additive’’ implies adding material to create an object, unlike the traditional method that requires milling, machining, or carving. The components and products in 3D manufacturing are easier to distribute and track — resulting in intelligent digital supply chains.
Blockchain can power up these developing technologies by eliminating security bottlenecks, protecting IP (intellectual property) from mishandling, and optimizing project management.
Genesis of Things is a company operating to join forces of 3D printing, blockchain, and IoT to launch the foremost production processes. Their distributed factory allows customers to collaborate with the best 3D printer for their manufacturing and securely move production files directly into a 3D printer, without human intervention. This platform brings value to users who have overloaded inventory with low turnover, costly management. Also, it’s helpful for companies who need to track the production processes regularly.
Online Gaming
By the end of 2020, the global gaming market is anticipated to reach US$159.3 billion. Gaming became a multi-billion dollar industry with its competitions, winners, cash rewards, and the black market.
Blockchain technology allows gamers to generate even more revenues by reselling their in-game items to other players or adding them to new digital worlds.
Online players typically buy the in-game components to boost their experience but cannot do anything further with the purchased items after the game is completed. For example, gaming company Polyient Games is going to transform the way gamers deal with the purchased items by recording them on the blockchain and then turning them into assets easily and securely converted into cash.
Food Safety
The food industry always aims to provide customers with the products of the highest quality to avoid strict regulatory fines. Spoiled food and beverages can cause severe poisoning and lead to severe infections such as Salmonella, Clostridium perfringens, or Colibacillosis. That’s why food businesses and CPG (consumer packaged goods) companies have to stick to all sanitary standards and requirements strictly.
Blockchain again comes into play to help manufacturers and retailers avoid these issues. It can allow managers to track the entire food supply chain and identify contamination cases. Most POS (point-of-sale) systems remove compromised and damaged goods from the chain and automatically will make a product recall. This way, retailers get and then sell only safe products to consume.
Simple QR codes on the goods can be the perfect blockchain-enabled solution for the industry. When scanned, it demonstrates the whole route of a product – from manufacturer to the supermarket.
Walmart uses a blockchain to make the end-to-end supply chain transparent and deliver only safe and quality food to customers.
In 2018, Walmart partnered with IBM and other food organizations and created a blockchain-driven food traceability network built on open-source technology. The platform allowed the retailers to track a product from the first to the final destination in just 2.2 seconds, which previously would take up to seven days. Walmart aims to adopt the technology to the full extent to minimize the number of consumers who get sick due to food incidents while at the same time decreasing losses for stores and suppliers during a recall.
Distributed databases, smart contracts, and immutability of the blockchain ecosystem make the technology a massive game-changer for many industries, as we see in this article.
The progressive companies are ready for transformation and many have started adopting DLT and reaping the benefits.
Among others, blockchain unveils the following opportunities for those who aren’t afraid of innovations:
1. Greater transparency and traceability of payments between multiple allies.
2. Secure management of digital relationships using smart contracts.
3. Fewer intermediaries and, therefore, massive cost savings.
4. Tracking and managing access to critical data in real-time.
5. Prevention of fraudulent activities and mishandling of data stored on the blockchain.
These are the most impactful benefits of employing DLT. If you seek groundbreaking technologies to power up your business and stay competitive in your sector, Innovecs is here to help implement your vision.
At Innovecs, our blockchain developers and engineers in the field build tailored blockchain software that allows businesses to grow with a forward-looking approach. We’d love to chat with you to find out what questions, concerns, or objectives you might have.