Will consumers refuse cash in favor of decentralized substitutes? How soon will the banking sector adopt blockchain in its financial software? What are the key obstacles that the financial industry faces while implementing this technology?
This post will answer these questions and shed some light on the fintech industry can benefit from blockchain.
To understand all the advantages that blockchain can provide across fintech, let’s figure out how exactly this technology works. 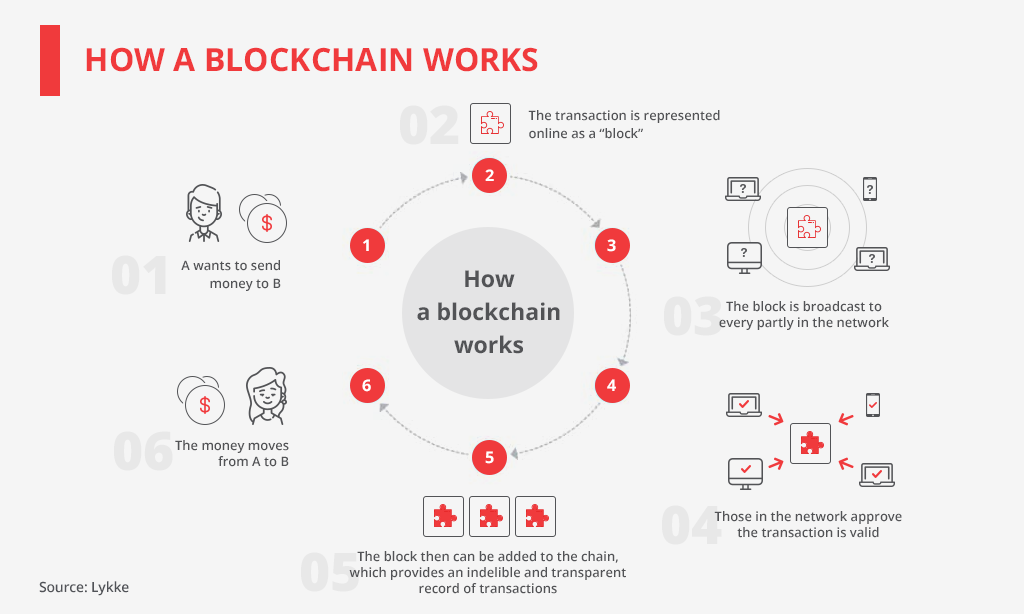
With the rush surrounding the speed of transactions, everyone is talking about Visa’s example as the best practice.
According to Visa, it can proceed as much as 56k transactions per second (tps); however, in reality, it is capable of no more than 1.7k tps.
What about blockchain? While Ethereum-based applications are limited to only 15 tps, EOS-driven solutions can handle almost 4k tps, which is more than twice as fast as Visa.
Among the factors that are restraining the speed of blockchain-led transactions, there are:
- The number of nodes in the network that are required to validate the transaction. A blockchain is a double-edged sword. With fewer witness nodes, the speed of transactions quickens, but it simultaneously makes the technology more centralized.
- The blockchain’s bandwidth. Every chain has its own bandwidth. However, some of them (e.g., EOS-based) allow side-chains to be built that incorporate into the major chain. It’s like building a bridge across a river to defuse a traffic jam.
So far, the speed of blockchain exceeds Visa, but it can be further improved, making the technology more appealing to the banking and the trading domains.
Transparency is a cornerstone of fintech credibility.
Even the housing crisis of 2008 was caused by a lack of transparency. It was difficult to track consumers’ ability to pay. This led to the ineffective management of the loan portfolio in the USA and resulted in the world’s economic depression.
How can blockchain help? A blockchain records every transaction, approves them with the help of its witness nodes, and then stores the data simultaneously on all its nodes. This procedure prevents any unauthorized activities.
In addition, blockchain can help financial institutions provide their customers with up-to-date loan portfolio information. Aided by its smart contracts, blockchain delivers reports only to authorized users, and since any new record must be approved by all the witness nodes, blockchain prevents data forging.
When it comes to the brokerage of transactions, a fee emerges.
For instance, the US mutual fund takes 1.44% from the operations turnover for its services.
Being naturally incorruptible, blockchain can serve as a distributed ledger that requires no third parties. As a result, the average cost of one Ethereum-based transaction is only $0.37 (source: CryptoSlate).
It’s interesting to know that in 2018, 52% of all frauds were carried out by employees inside the organization.
One high-profile case within fintech was a $2 billion loss endured by the Indian bank PNB in 2018. Two bank employees allowed one of the largest Indian jewelers to import supplies from Hong Kong by guaranteeing its payments by letters of undertaking. The jeweler gave the bank no required documents, and once the supplier requested payment, the jeweler couldn’t shoulder its liabilities.
Smart contracts on top of blockchain could prevent such cases by approving transactions only when all the requirements are accomplished.
Although blockchain can improve fintech, financial institutions are cautious about adopting this technology.
The industry resistance and regulatory limitations are major obstacles in blockchain adoption across the financial domain.
While some countries like Japan, Switzerland, and Estonia recognized themselves as blockchain-friendly, there is still a list of territories with an uncertain attitude toward blockchain. Unless risks and instability factors aren’t solved at the global level, the fintech sector will remain a bit hostile toward any mind-boggling changes.
Some financial institutions understand the advantages of distributed ledgers and have already launched new projects within their industry. Let’s analyze the latest ones.
In 2018, Bank of America filed a patent to develop “ATM as a service” built with blockchain technology. Being faster than Visa, blockchain will be able to speed up transactions while keeping all operations secured. It will also allow ATMs to be used not only for cash withdrawals and inter-network transactions but even to access point-to-point communications.
Trading is another realm that can benefit from blockchain. In January 2019, the China Banking Association, headed by 10 major banks of the country, announced the launch of a new blockchain-driven trade platform. It aims to facilitate trade transactions in a decentralized way.
When it comes to the startups operating within fintech, it’s possible to talk about a variety of solutions from around the market.
For instance, if you’re looking for examples of any blockchain-led payrolls, you can choose between PayMe and Etch. Their smart contracts allow transferring remittances instantly once the work is done and approved.
MyEG, the company working on PayMe, has already received the e-money license from Bank Negara Malaysia. By September 2019, the developer plans to deliver an e-wallet with secured payments crafted on top of blockchain.
Innovecs is also about to start a new fintech project based on blockchain technology. So, if you need any help finding a solution, feel free to contact us.
Distributed ledgers, smart contracts, and invulnerability of blockchain make the technology a potential game-changer for the financial sector. However, regulatory limitations and the financial industry’s resistance curb the implementation of innovative financial technology solutions.
Against this background, the companies that are ready to transition are unveiling new opportunities while others are standing behind.
If you are a groundbreaker in need of help implementing your vision, Innovecs is here to assist.
At Innovecs, we build blockchain software that allows businesses to succeed and customize the user experience. Just drop us a line and receive comprehensive advice on how to adopt decentralized technology.